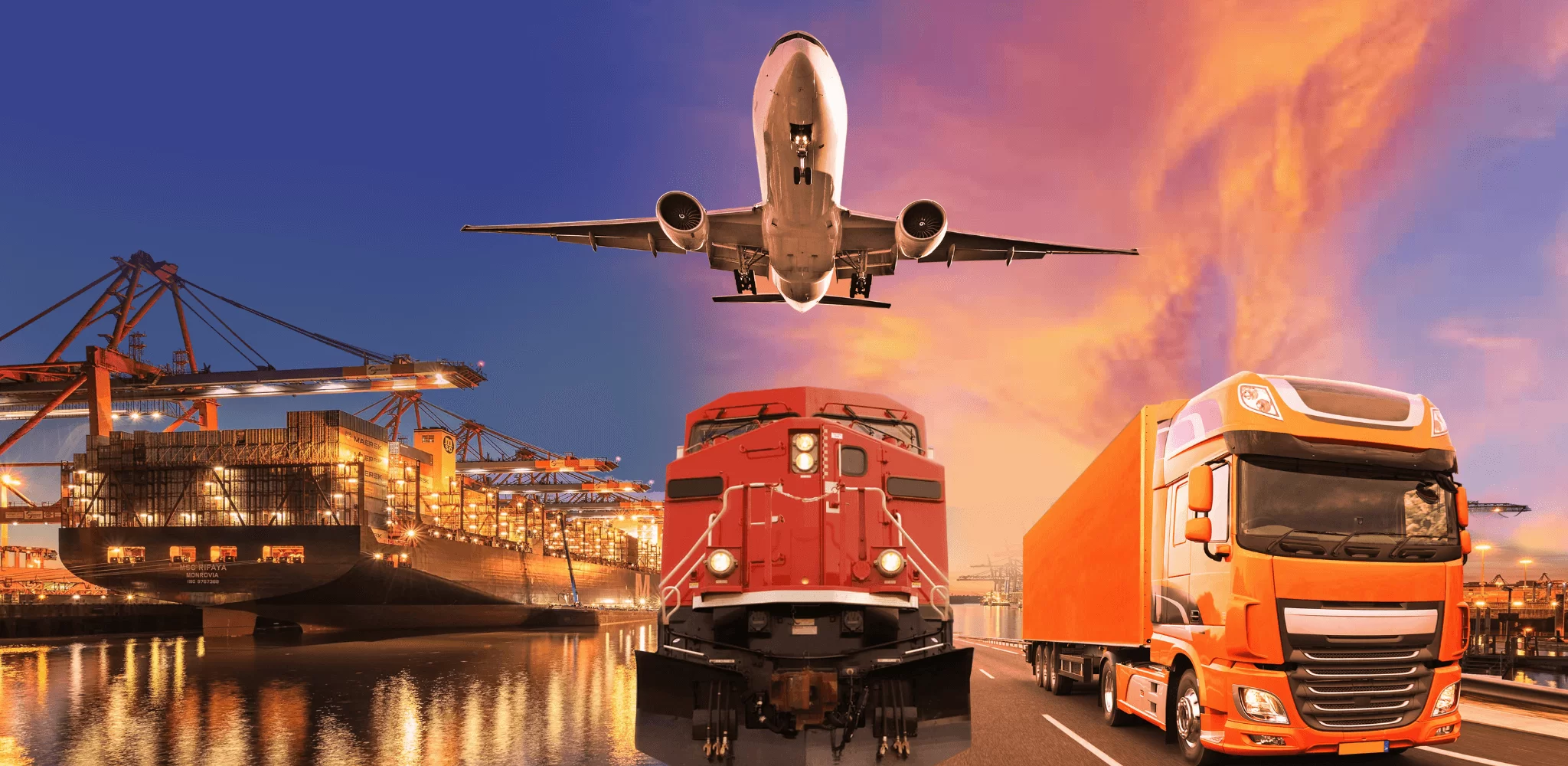
In the bustling world of logistics and transportation, efficiency and sustainability are the twin pillars that uphold the seamless movement of goods across vast distances. One key strategy that continues to gain prominence in this realm is intermodal transportation.
This innovative approach involves the seamless transfer of cargo between different modes of transportation, such as trucks, trains, and ships, to capitalize on their respective strengths. Let’s delve into the advantages of intermodal transportation and how it’s reshaping the landscape of freight movement.
Enhanced Efficiency:
One of the standout advantages of intermodal transportation is its ability to enhance efficiency. By seamlessly transitioning between various modes of transport, intermodal systems optimize each leg of the journey based on factors like cost-effectiveness, speed, and capacity.
For instance, a shipment might start its journey on a truck for short-haul distances, then seamlessly transfer to a train or ship for long-haul segments. This flexibility ensures that goods reach their destination swiftly and economically, minimizing delays, maximizing productivity and creating truck driving jobs.
Moreover, by utilizing multiple modes of transport, intermodal systems mitigate the risk of disruptions due to factors like road congestion or adverse weather conditions, further enhancing reliability.
Cost Savings:
Intermodal transportation offers significant cost savings compared to traditional methods. By leveraging the strengths of different modes of transport, companies can optimize their shipping routes to minimize expenses while maximizing efficiency.
For example, transporting goods via rail over long distances tends to be more cost-effective than relying solely on trucks. Additionally, intermodal transportation reduces fuel consumption and carbon emissions by maximizing the utilization of more fuel-efficient modes of transport, such as trains and ships.
These cost-saving benefits translate into improved profitability for businesses and potentially lower prices for consumers.
Environmental Sustainability:
In an era where environmental concerns loom large, intermodal transportation emerges as a sustainable solution for freight movement. By shifting freight from roadways to railways and waterways, intermodal systems reduce congestion and greenhouse gas emissions associated with truck transportation.
Trains and ships are inherently more fuel-efficient and emit fewer pollutants per ton-mile compared to trucks. This transition to greener modes of transport aligns with global efforts to curb carbon emissions and combat climate change.
Moreover, intermodal transportation facilitates the consolidation of cargo, reducing the overall number of vehicles on the road and further mitigating environmental impact.
Improved Safety:
Safety is paramount in the transportation industry, and intermodal systems offer notable advantages in this regard. By minimizing reliance on long-haul trucking, intermodal transportation reduces the likelihood of accidents and incidents on congested highways.
Trains and ships adhere to strict safety protocols and are equipped with advanced technologies to ensure the secure transportation of goods. Additionally, intermodal terminals are designed with safety in mind, featuring state-of-the-art infrastructure and procedures to streamline the transfer of cargo between different modes of transport.
By prioritizing safety at every stage of the journey, intermodal transportation enhances overall industry standards and fosters a secure operating environment for all stakeholders.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, intermodal transportation stands as a beacon of efficiency, sustainability, and safety in the realm of logistics and freight movement. By seamlessly integrating different modes of transport, businesses can unlock cost savings, enhance efficiency, and reduce their environmental footprint.
As the demand for efficient freight solutions continues to grow, intermodal transportation will play an increasingly vital role in shaping the future of the industry.